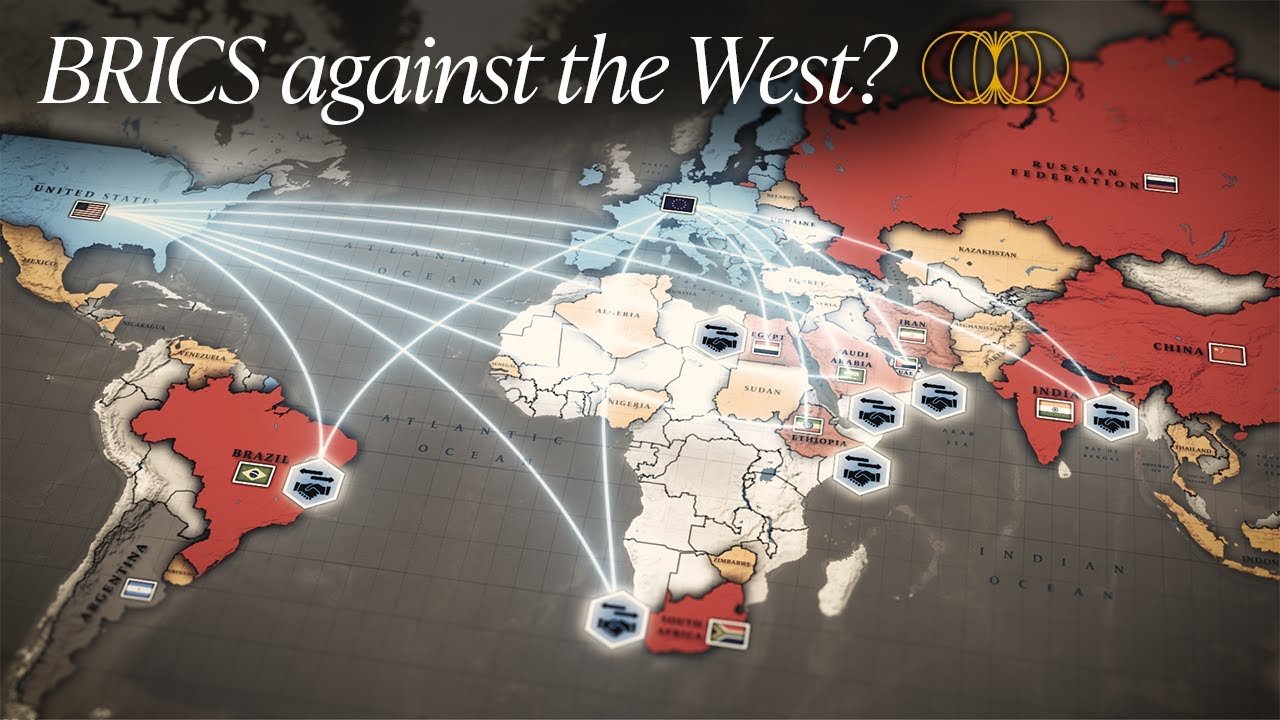
In August 2023, the BRICS group, initially comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, announced a significant expansion to include six new members: Argentina (which later withdrew), Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates, nearly doubling its size. This move has sparked varying interpretations among global observers, with some viewing it as a shift towards a more multipolar world challenging Western dominance, while others question the coherence and impact of the expanded BRICS. The expansion reflects the group’s desire to reform global governance and increase the representation of emerging economies, amidst growing economic contributions and a shared interest in reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade.
- The BRICS summit in Johannesburg in August 2023 announced the expansion of the group, adding six new countries, aiming to nearly double its size.
- Despite Argentina’s initial interest, it later withdrew its application, influenced by its new president’s stance on international policies.
- The expansion has been interpreted as a victory for China and a challenge to US leadership, with up to 40 countries expressing interest in joining BRICS.
- BRICS aims to reform global governance, promote multilateralism, and provide a voice for emerging economies, reflecting dissatisfaction with the existing world order dominated by Western institutions.
- The group’s economic influence has grown, with its share in global GDP and trade increasing, while the share of G7 economies has declined.
- New members, particularly oil-rich nations, enhance BRICS’s role in global oil supply and demand, shifting the balance of economic power.
- Internal interests and the pursuit of de-dollarization in international trade are key motivations behind the expansion, with China and India seeking to trade oil in their own currencies.
- Despite proposals for a common BRICS currency, practical challenges and the pursuit of national interests over collective goals have limited progress on such initiatives.
- The inclusion of countries with significant political and territorial disputes raises questions about the coherence and unity of the expanded BRICS.
- Russia’s and Iran’s memberships highlight the challenges of aligning the group’s stated mission of promoting global peace and stability with the actions of its members.
- The expansion serves as a signal to the West about the need for reforming global governance systems to better reflect the interests of the global South.
- Despite its ambitions, the BRICS group’s effectiveness in transforming the global order remains limited by its internal contradictions and the dominant role of China.
- The G20 is suggested as a more viable platform for exploring new ideas for global governance, representing a broader spectrum of the world’s major economies.
“Channel tackling global issues from the fields of geopolitics, international relations, economy, technology, which shape the world of today.”
Official website: patreon.com/gtbt
Original video here.
This summary has been generated by AI.
Leave a Reply